An all-electric vehicle in India or an EV has rechargeable electrical energy storage on-board that works as a source of energy. For the electric motor, which moves or drives the vehicle. It does not have any conventional internal combustion (IC) engine that burns fuel or gas for the propulsion of the vehicle. An EV does not burn any fuel for propulsion thus it does not have any tailpipe exhaust.
An electric vehicle in India can be charged using a charging unit called EV chargers plugged into an external source of electric power. You can charge your EV using a slandered 120v outlet at home. You can also charge your EV at a dedicated charging station that will charge a vehicle faster than a home charger. While you are outdoors by paying some extra then that cost you charging at home. EV vehicles in India also use a regenerative braking system, which generates electricity by slowing down the vehicle when applied brake. The energy generated from the regenerative braking system is either stored in batteries or directly used by vehicles.
The range of an electric vehicle depends on the vehicle itself. Because every model or company has different batteries that have a different range. And, it also depends on the performance of the vehicle. An all-electric vehicle can run non-stop for a normal journey that is around 180km. Unless the weather conditions or not extreme because of extreme temperature.
Working of an electric vehicle or EV
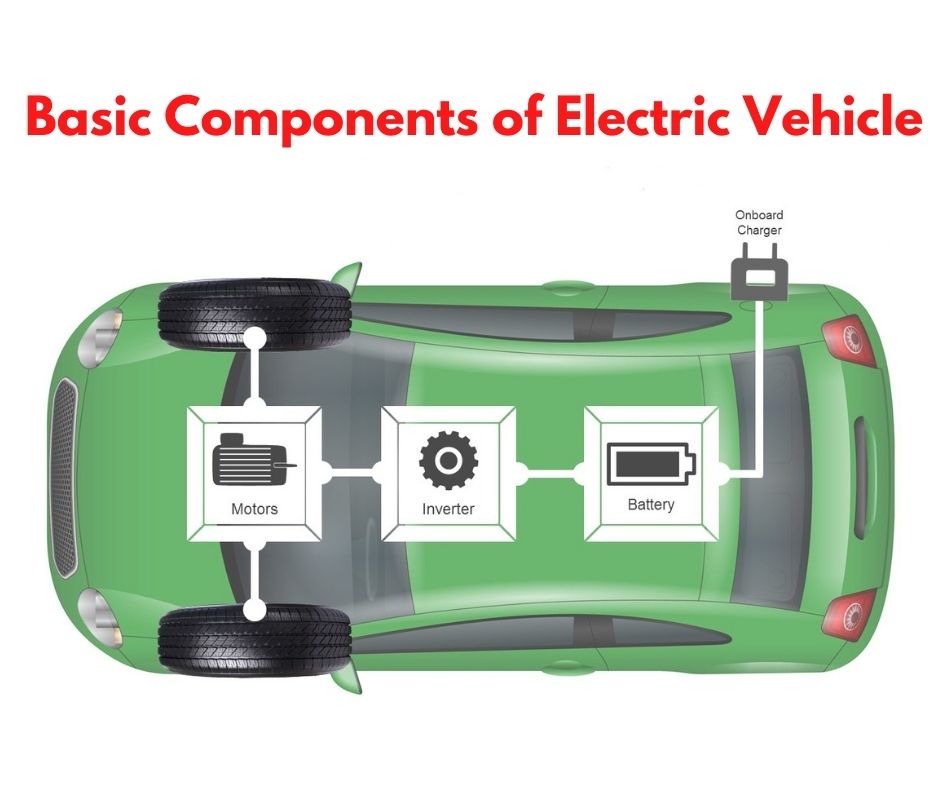
All-electric vehicle has four basic components that make an electric vehicle work or move.
- Energy storage units (high capacity batteries)
- Inverter
- AC/DC motor
- Controller
Energy storage units are the high capacity batteries or supercapacitors that store the energy onboard. Currently, the most common method used by electric vehicle manufacturers is storing energy in chemical form; The battery work as a source of power to the electric motor in the vehicle. All the batteries in the vehicle are managed by BMS (Battery Management System).
The inverter is a device that converts the DC (direct current) to AC (alternating current) for the AC motor. The battery supply the power in direct current thus an inverter required to convert it to alternating current.
Electric Motor, the electric vehicle manufacturers uses both alternating currents (AC) motor and direct current (DC). The motor in electric vehicles converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. The mechanical energy generated by an electric motor is transferred to the wheels by a single-speed transmission.
The controller acts as a gateway to the motor and controls the flow of the electrical energy delivered by the batteries. AC Motor controls the speed of the electric motor and it also controls the energy required by other components. It is the brain of the electric vehicle.
Other components that contribute to the working of an electric vehicle
- Charging port
- On-board charger
- Thermal system
Charging port, it used to charge the on-board chemical batteries by connecting to an external energy source.
On-board chargers, some of the vehicles have the alternating current motor, which can be used for the regeneration of electrical energy. The energy generated by an AC motor is first converted into direct current. By the onboard charger and stored in batteries or used by vehicles directly. This technology has increased the range of EVs.
The thermal system, the electric motor produces heat, which leads to more use of energy and reduces the range of the vehicle. The cooling system helps in maintaining operating temperature for an electric motor, and other components.
These components work together to make an electric car work or run.

